THE PRINCIPLES OF NEW URBANISM
The principles of New Urbanism can be applied increasingly to projects at the full range of scales from a single building to an entire community.
1. Walkability
-Most things within a 10-minute walk of home and work
-Pedestrian friendly street design (buildings close to street; porches, windows & doors; tree-lined streets; on street parking; hidden parking lots; garages in rear lane; narrow, slow speed streets)
-Pedestrian streets free of cars in special cases
2. Connectivity
-Interconnected street grid network disperses traffic & eases walking
-A hierarchy of narrow streets, boulevards, and alleys
-High quality pedestrian network and public realm makes walking pleasurable
3. Mixed-Use & Diversity
-A mix of shops, offices, apartments, and homes on site. Mixed-use within neighborhoods, within blocks, and within buildings
-Diversity of people – of ages, income levels, cultures, and races
4. Mixed Housing
A range of types, sizes and prices in closer proximity
5. Quality Architecture & Urban Design
Emphasis on beauty, aesthetics, human comfort, and creating a sense of place; Special placement of civic uses and sites within community. Human scale architecture & beautiful surroundings nourish the human spirit
6. Traditional Neighborhood Structure
-Discernable center and edge
-Public space at center
-Importance of quality public realm; public open space designed as civic art
-Contains a range of uses and densities within 10-minute walk
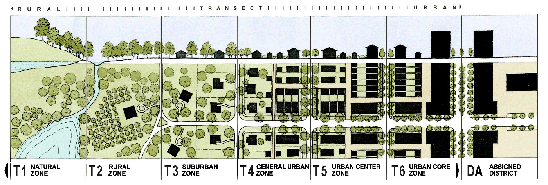
-Transect planning: Highest densities at town center; progressively less dense towards the edge. The transect is an analytical system that conceptualizes mutually reinforcing elements, creating a series of specific natural habitats and/or urban lifestyle settings. The Transect integrates environmental methodology for habitat assessment with zoning methodology for community design. The professional boundary between the natural and man-made disappears, enabling environmentalists to assess the design of the human habitat and the urbanists to support the viability of nature. This urban-to-rural transect hierarchy has appropriate building and street types for each area along the continuum.
|
More information on the transect
7. Increased Density
-More buildings, residences, shops, and services closer together for ease of walking, to enable a more efficient use of services and resources, and to create a more convenient, enjoyable place to live.
-New Urbanism design principles are applied at the full range of densities from small towns, to large cities
8. Smart Transportation
-A network of high-quality trains connecting cities, towns, and neighborhoods together
-Pedestrian-friendly design that encourages a greater use of bicycles, rollerblades, scooters, and walking as daily transportation
9. Sustainability
-Minimal environmental impact of development and its operations
-Eco-friendly technologies, respect for ecology and value of natural systems
-Energy efficiency
-Less use of finite fuels
-More local production
-More walking, less driving
10. Quality of Life
Taken together these add up to a high quality of life well worth living, and create places that enrich, uplift, and inspire the human spirit.